1. Dobra jakość za rozsądną cenę
Nie oszukujmy się – podróże do najtańszych hobby nie należą. Nawet te relatywnie bliskie. Człowiek jest na urlopie, delektuje się wolnym czasem i w związku z tym swobodniej niż na codzień wydaje pieniądze. Oczywiście można wybrać opcję totalnej taniości: namiot na bezdrożach, autostop, konserwy. My jednak wychodzimy z założenia, że wakacje są po to, by w pełni wypocząć, nie stresować się i poluzować zaciśnięty nierzadko przez pozostałe miesiące pas. Dlatego staramy się by wilk był syty, a i owca cała – tam gdzie ma to sens to oszczędzamy, ale zdarza nam się poszaleć z odrobiną luksusu, zwłaszcza gdy chodzi o nietypowe atrakcje lub ciekawe potrawy.
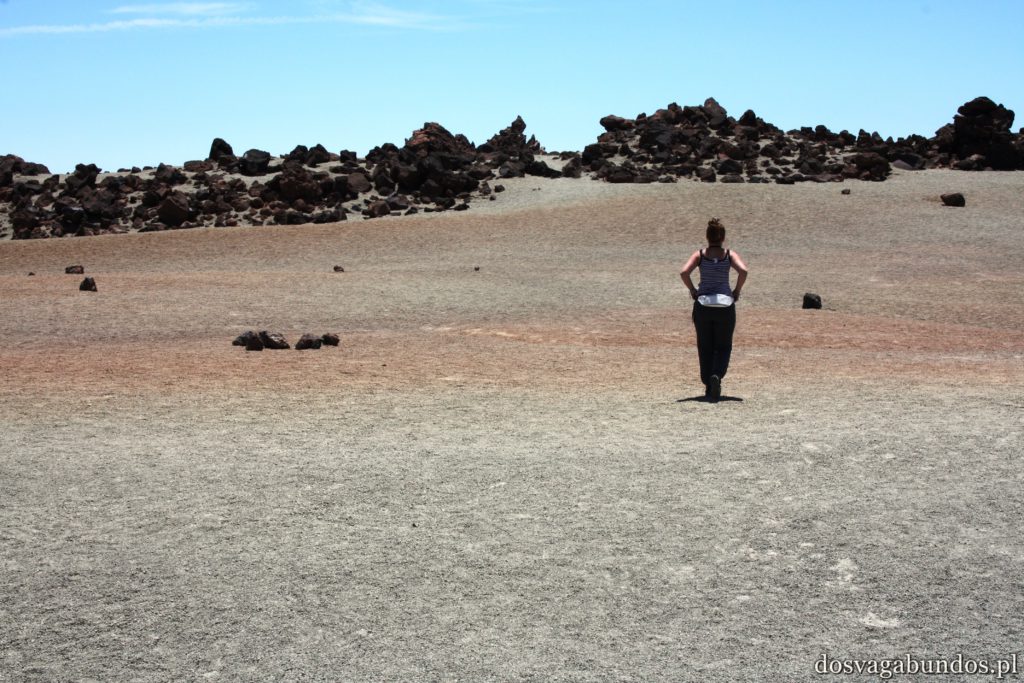

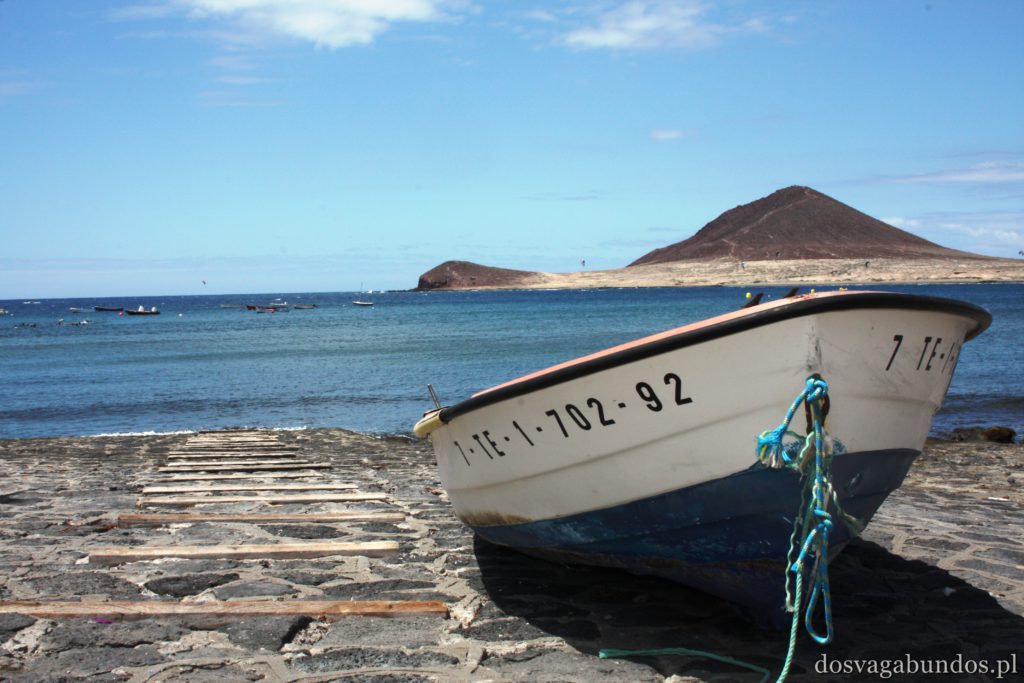
Na Teneryfę dotarliśmy z wycieczką. Biuro podróży gwarantowało przelot, pełne wyżywienie włącznie z lokalnymi alkoholami serwowanymi do posiłków i tydzień hotelowych noclegów za ok 1500zł od osoby. Na miejscu całe dnie zwiedzaliśmy, jeżdżąc wypożyczonym jeszcze w Polsce samochodem, wzdłuż i wszerz wyspy, więc zupełnie jakbyśmy zorganizowali sobie wszystko na własną rękę, z tą różnicą, że większość spraw logistyczno- technicznych ogarniał za nas ktoś inny. Wieczorami docieraliśmy do pokoju tak wykończeni, że zaraz po kolacji zasypialiśmy niemalże w ubraniach na łóżku, nie obcowalismy więc nawet w minimalnym stopniu z folklorem typu animacje czy dyskoteki.
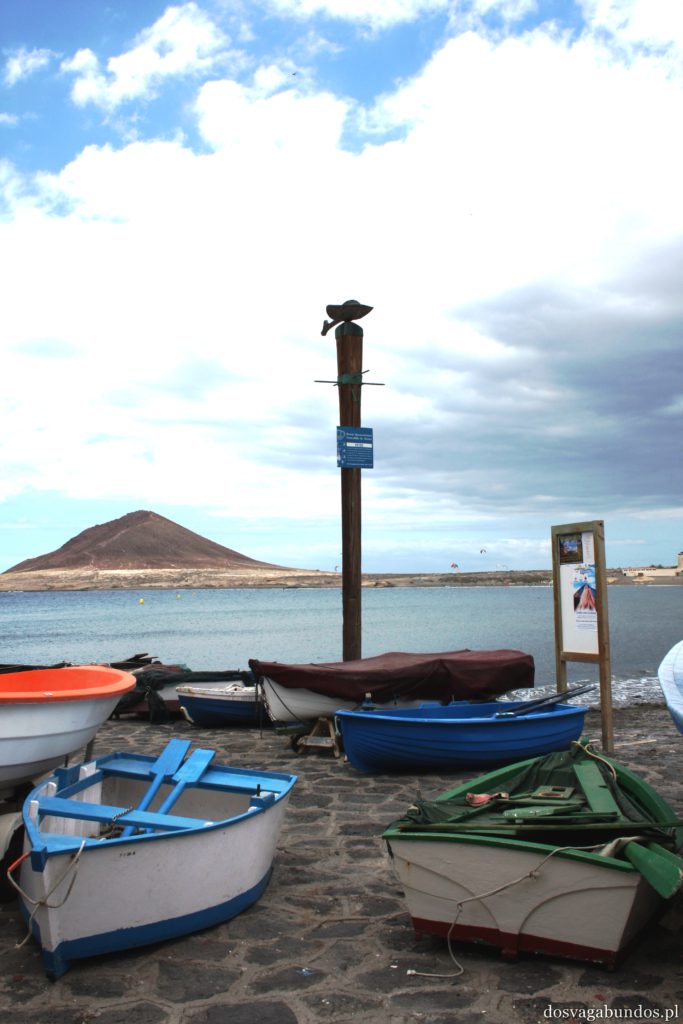

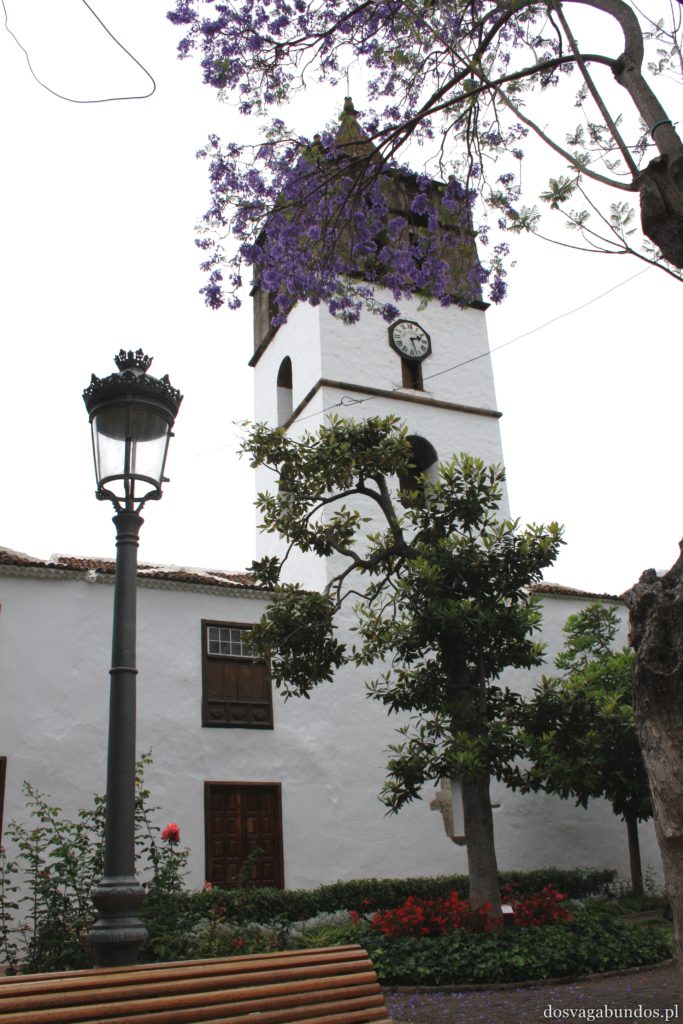
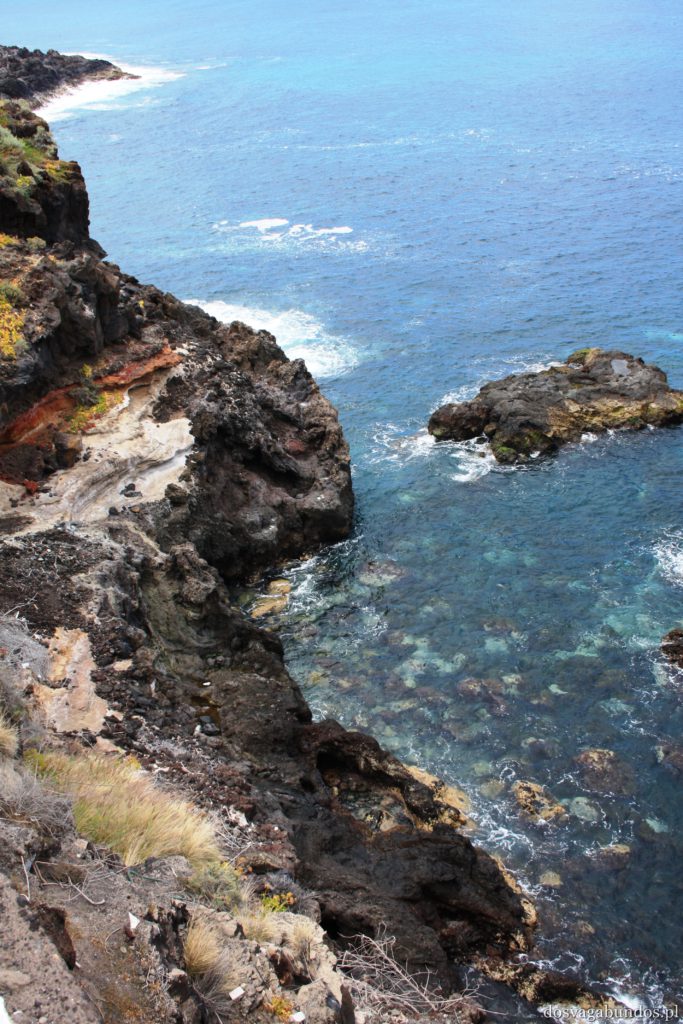
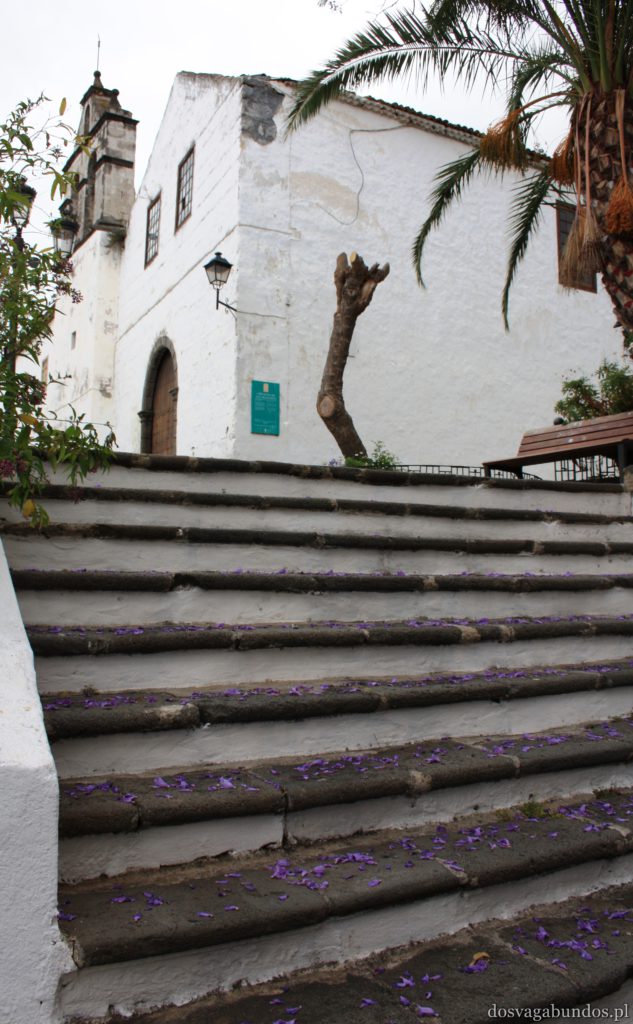
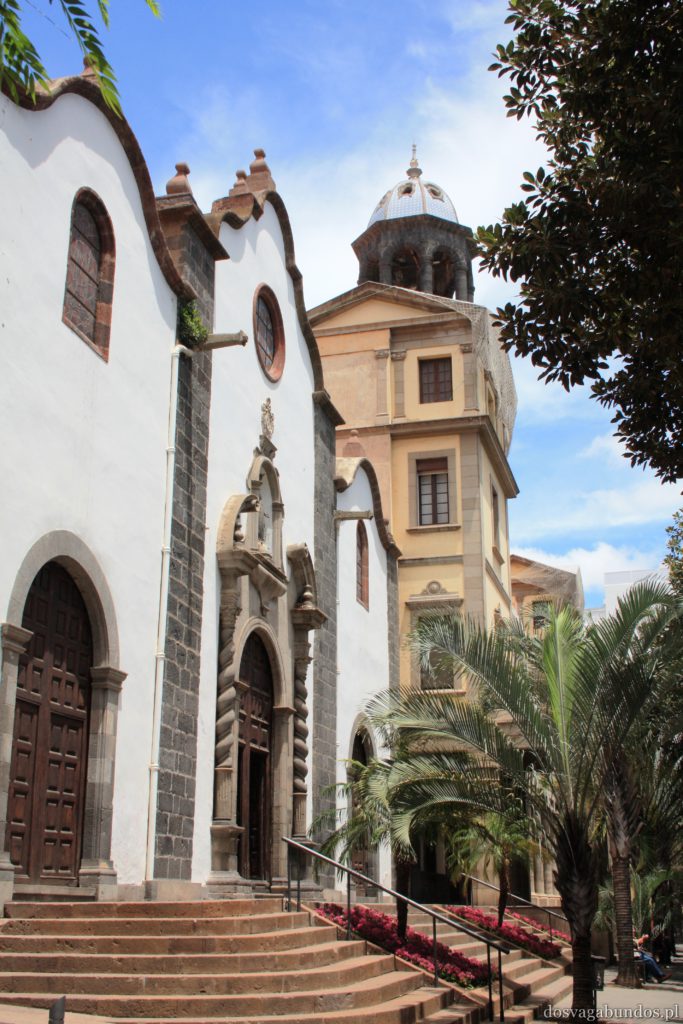
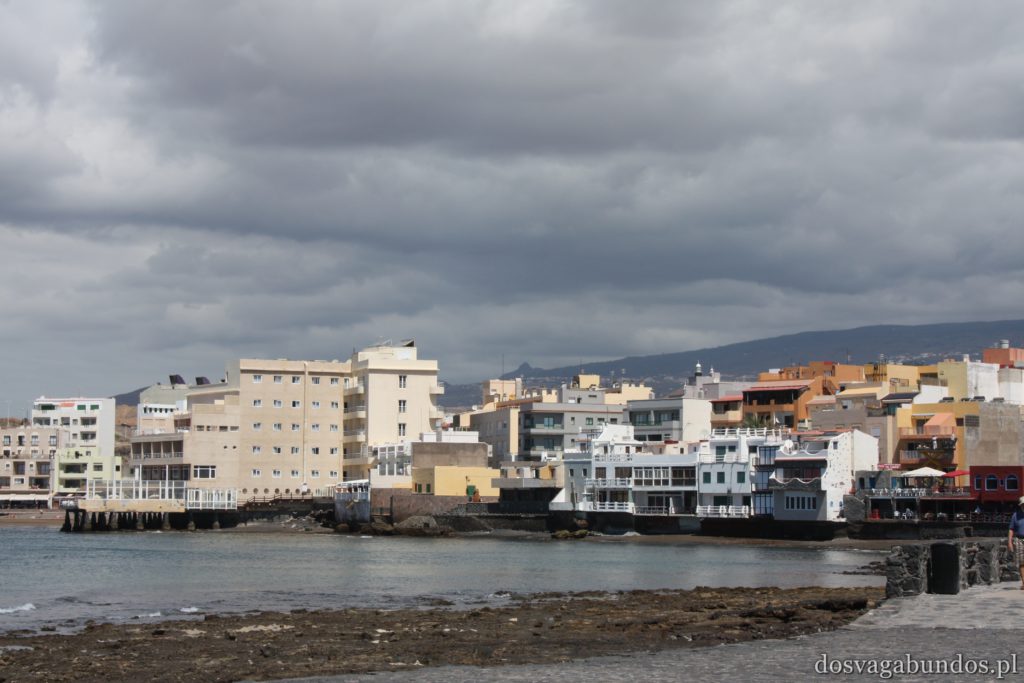
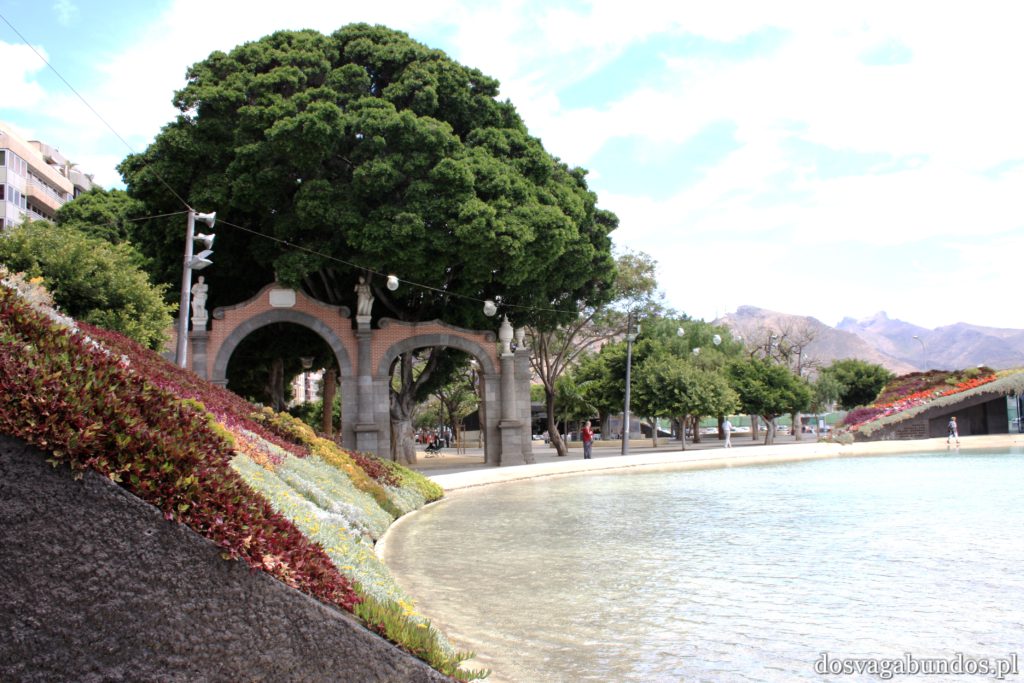
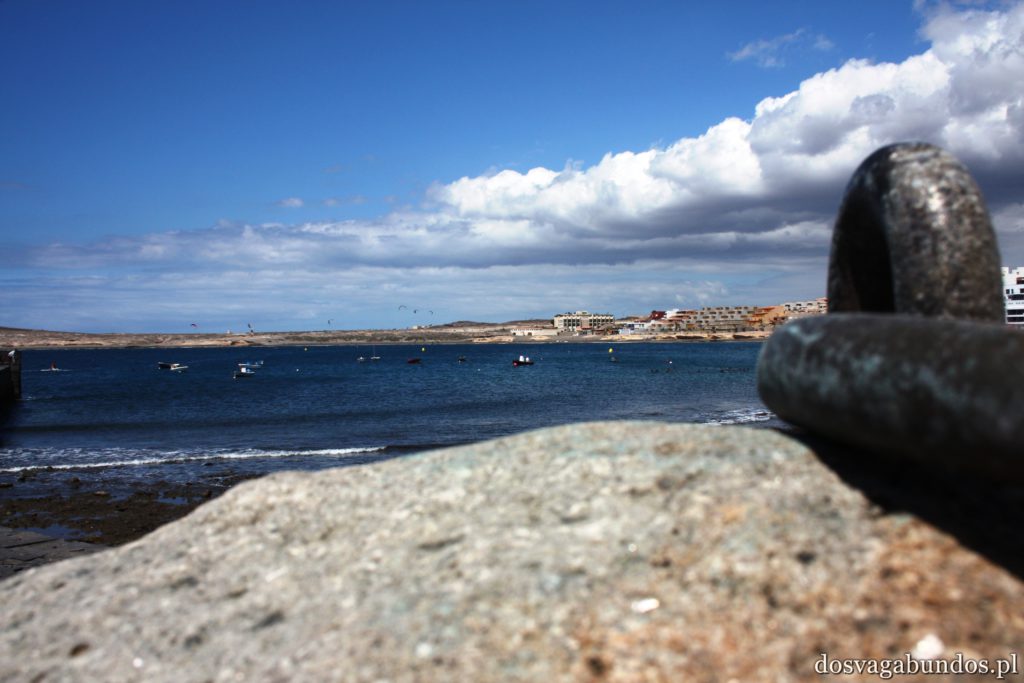
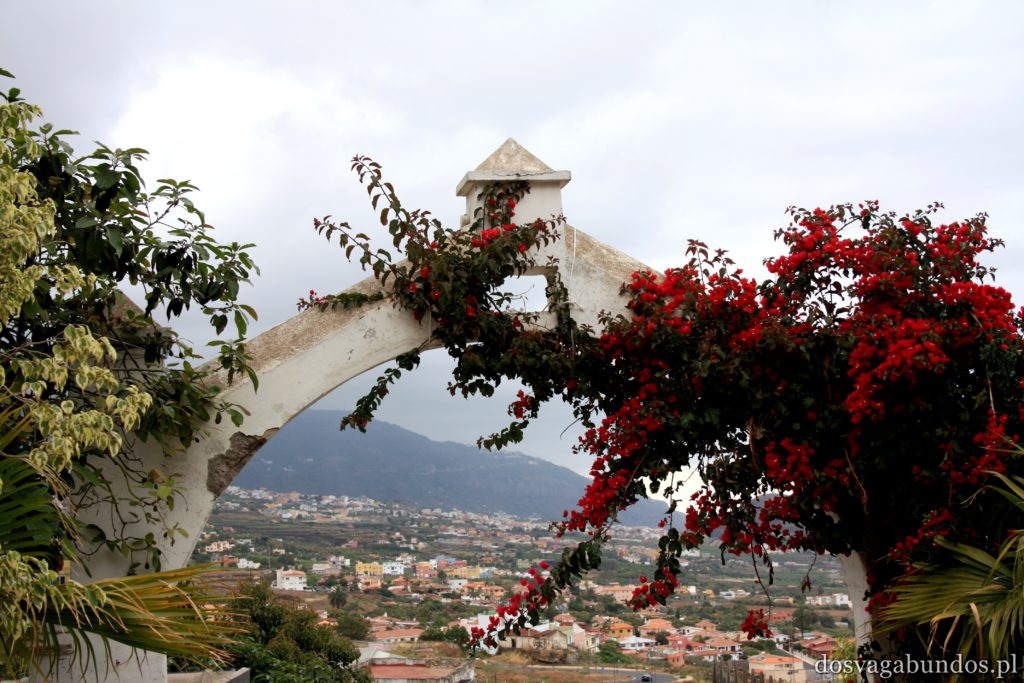
Pogoda do zwiedzania jest zazwyczaj idealna – nie za gorąco, nie za sucho, nie za wilgotno, jak to bywa w mocno egzotycznych miejscach. Czasami tylko, w wyższych rejonach, dość chłodno, ale wrzucone do plecaka spodnie dresowe i bluzy w pełni ten problem rozwiązują. Plaże czyste, niektóre sklaisto-kamieniste, inne z delikatnym piaskiem, dużo tropikalnej roślinności. Sporo do zobaczenia i jeszcze więcej do odkrycia – warto uważnie obserwować pobocza dróg, bo czasem można natrafić na prawdziwe, turystyczne perełki. Nam się udało namierzyć, w drodze do stolicy kraju, ukrytą w skałach rodzinną restaurację z domowym jedzeniem tak pysznym i świeżym, że do tej pory na myśl o nim uśmiechamy się pod wąsem! Generalnie z wycieczki na Teneryfę zadowoleni będą i sportowcy , i koneserzy architektonicznych cudów – piękne kolonialne zabudowy, i rodziny z dziećmi. Do tego relatywnie blisko – niecałe 6h z Warszawy (w porównaniu z prawie 12 h do Brazylii to jak z bicza strzelił).
2. Pyszna kuchnia
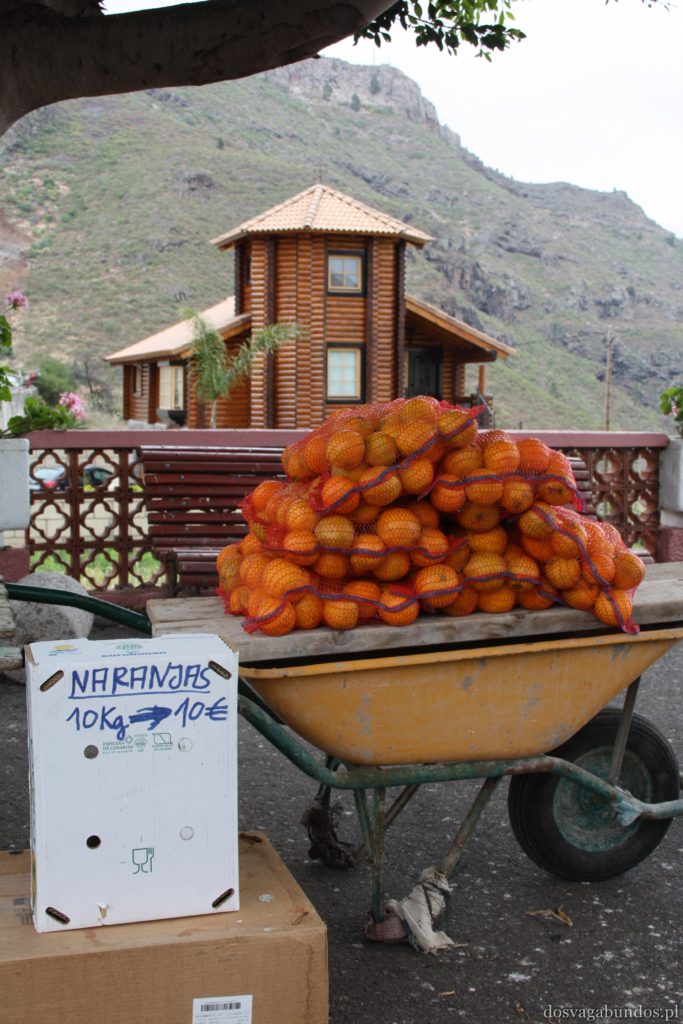
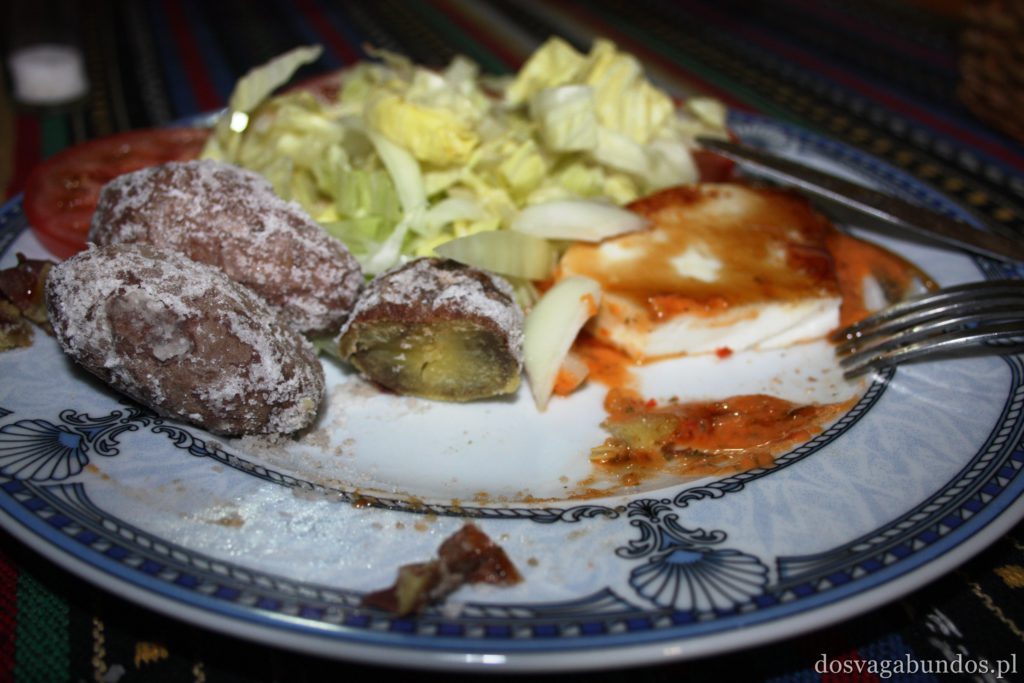
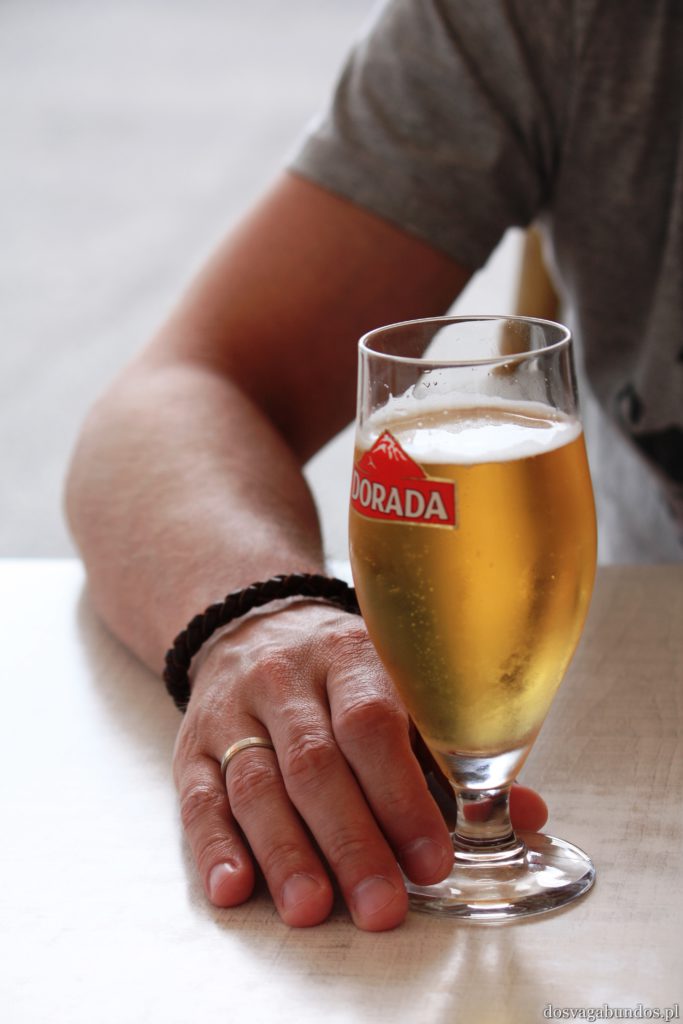
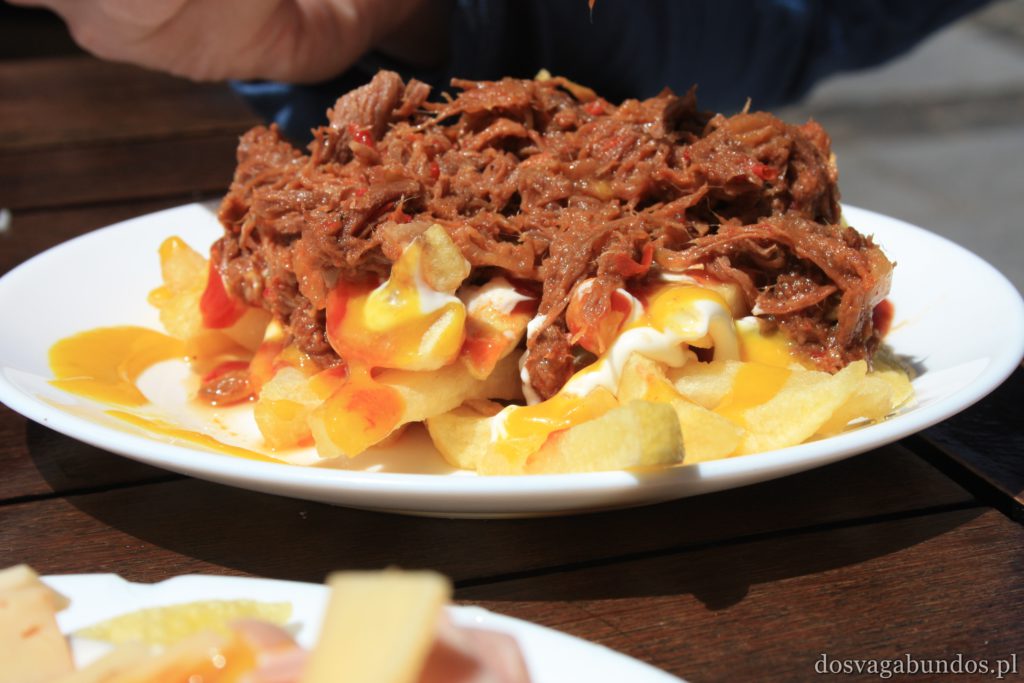
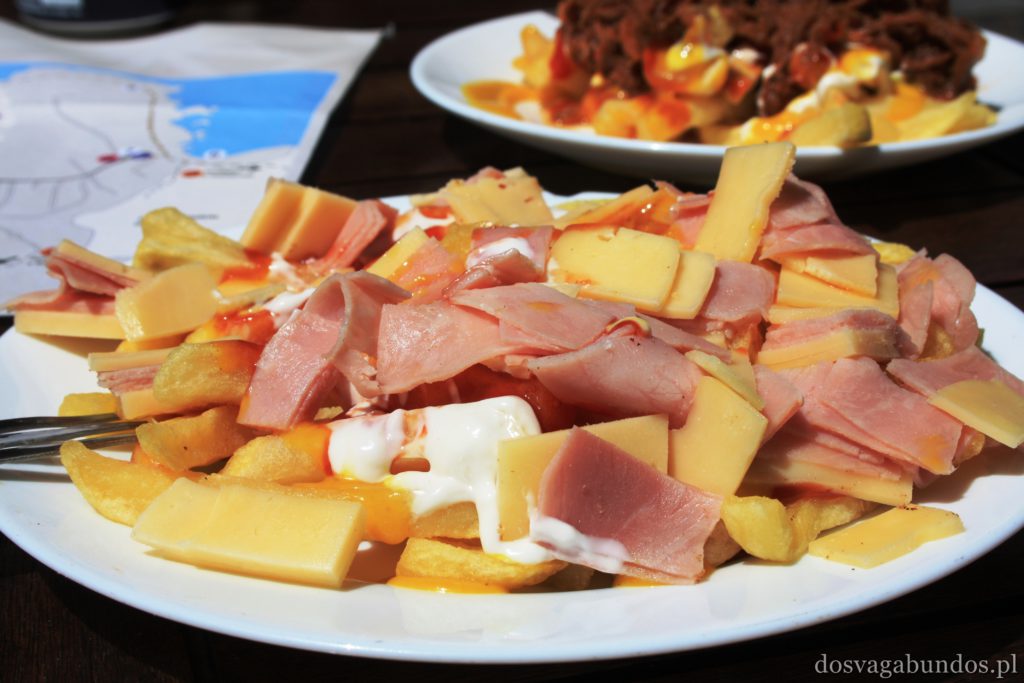
Werdykt nie mógłby być inny – jesteśmy wielkimi fanami ryb, owoców morza i…ziemniaków, a właśnie te składniki królują na kanaryjskich stołach. Naszą ulubioną odsłoną pyr były papas arrugadas, gotowane w mudurkach i bardzo mocno osolonej wodzie, serwowane z różnymi wariacjami sosów mojos, robionych na bazie octu, oliwy, czosnku i różnych przypraw. Gatunków ryb multum, nie do powtórzenia, wszystkie pyszne. Zazwyczaj serwowane a la pancha, czyli z rusztu, no i tradycyjnie smażone. Mają też sporo zup, do których dość często dodaje się sproszkowane gofio, tamtejszą mąkę, mającą tyle pozytywnych właściwości, co Amol. Płynne potrawy są sycące, zwłaszcza w formie gulaszy np. puchero canario lub potaje de berros. Owszem, zdarzają się i wtopy, takie jak np. low costowa wersja typowego kanaryjskiego dania (znanego również na Kubie), czyli ropy viejy. Nazwa dość osobliwa, bo w wolnym tłumaczeniu danie oznacza “stare ubranie”. W rzeczywistości jest to gotowana wołowina, która wygląda jakby na przyrządzony z niej gulasz rzuciło się stado wygłodniały psów, a po wstępnym przeżuciu wypluło kawałki mięsa na jakiś dodatek skrobiowy (jak to się pięknie określa frytki czy kasze w stołówkach pracowniczych). W smaku dobre, zwłaszcza, że fajnie je przyprawiają. Tylko walory estetyczne mocno kuleją. Nam zaserwowali raz porcję z szynką, ale nie żadną tam serrano, tylko chamską konserwą, do tego obficie zlaną keczupem i majonezem. Smakowało tak, jak wyglądało. Oprócz tej słabizny wszystko inne było na wysokim, smakowym poziomie. Oczywiście spodziewajcie się również typowych przedstawicieli kuchni hiszpańskiej – zatrzęsienie tapasów, mnóstwo świeżych owoców morza, paella, sery, kiełbasy, soczyste cytrusy i warzywne giganty, polewane oliwą i gęstym octem balsamicznym… wymieniać możnaby bez końca. Do tego alkohole – delikatne piwo Dorada, wino tinto, sangria, rum, aguardiente, czyli coś podobnego do włoskiej grappy (byle nie w opcji z ziołami, bo wtedy smakuje jak syrop na kaszel), no i last, but not least ulpekowaty ronmiel – likier na bazie rumu z dodatkiem miodu palmowego.
3. Różnorodność krajobrazu
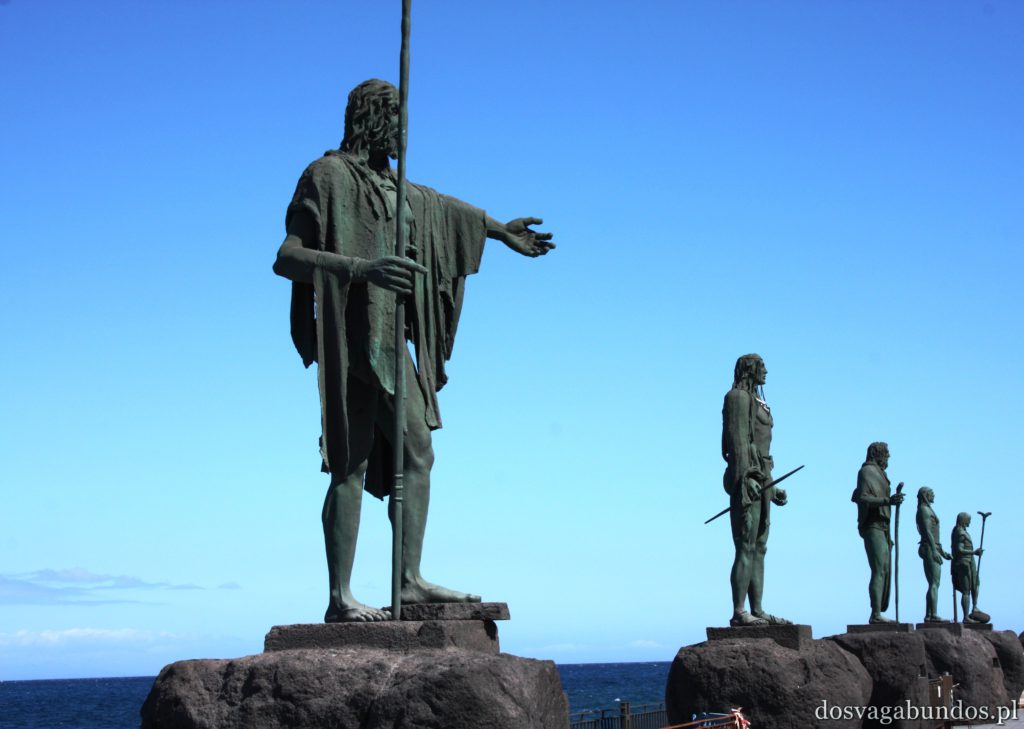
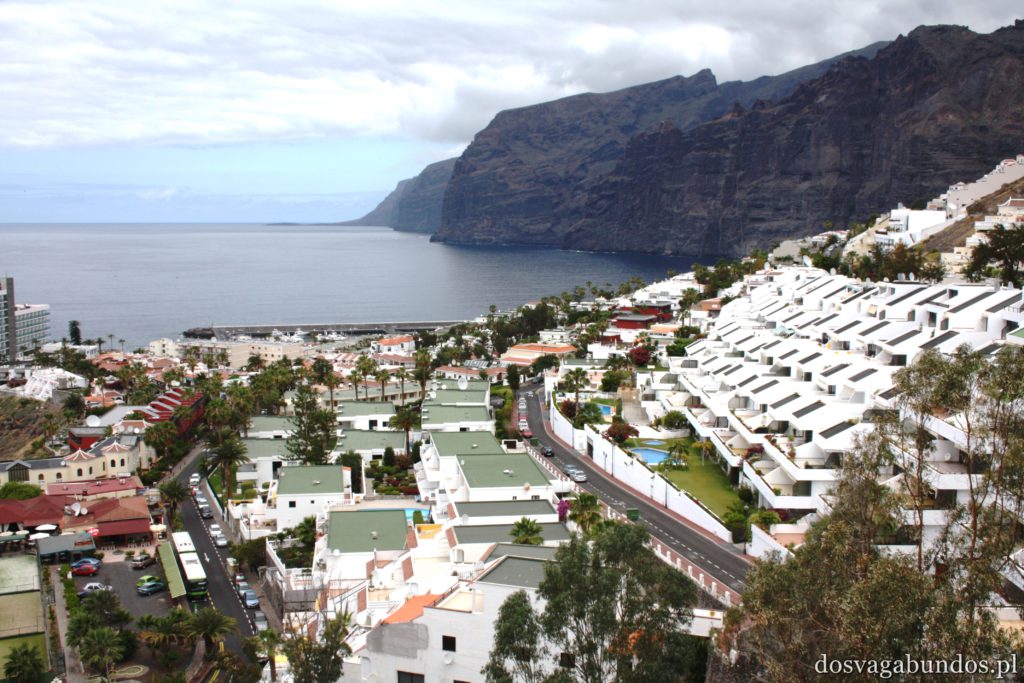
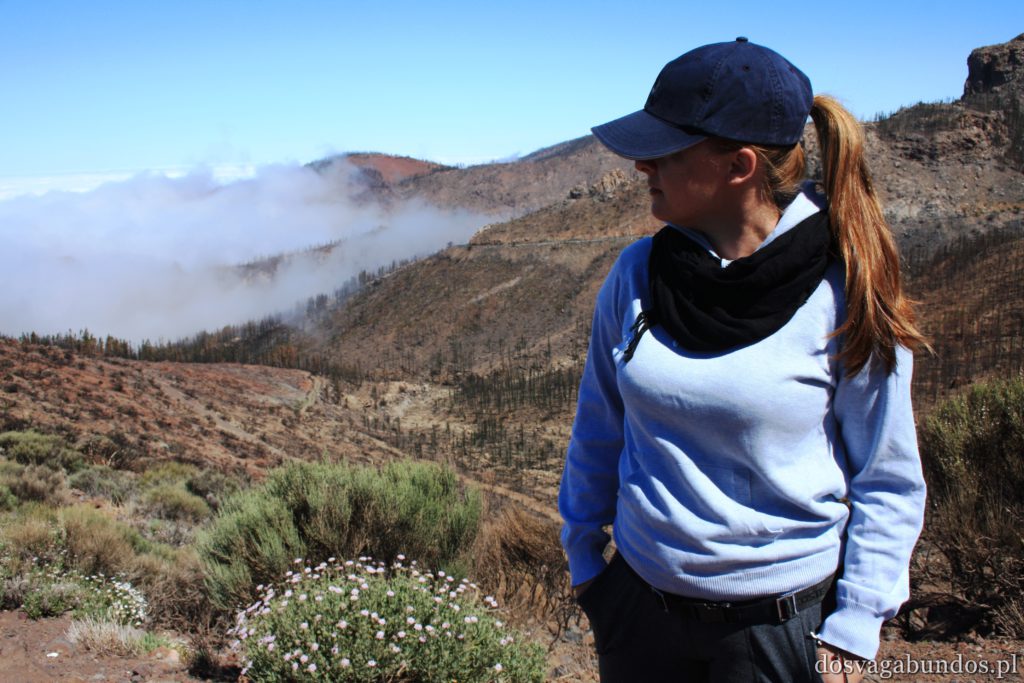
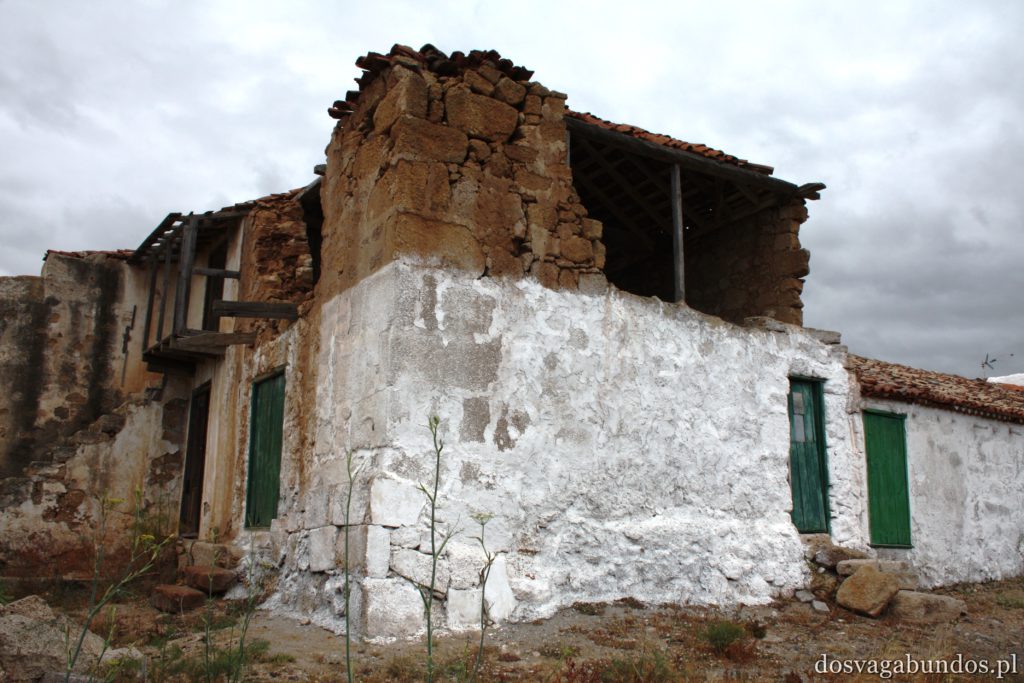
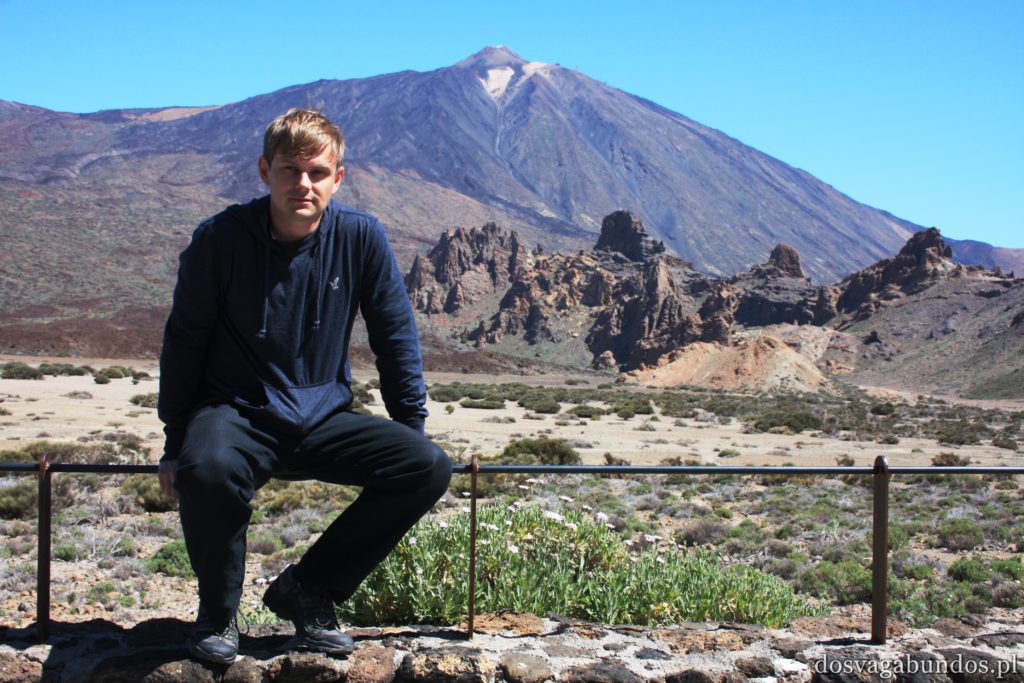
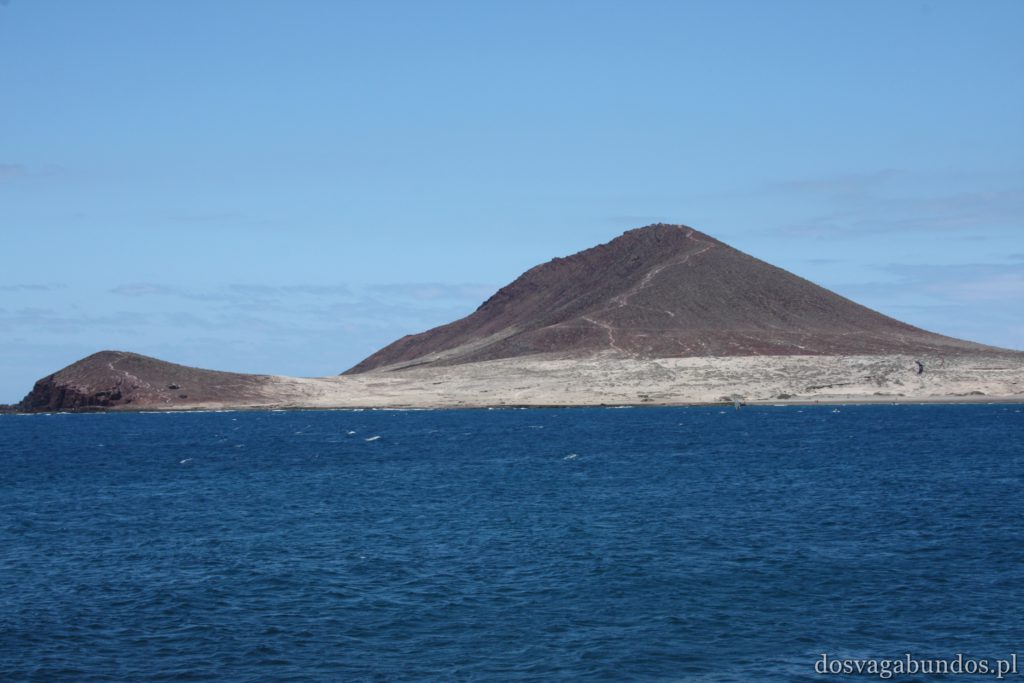
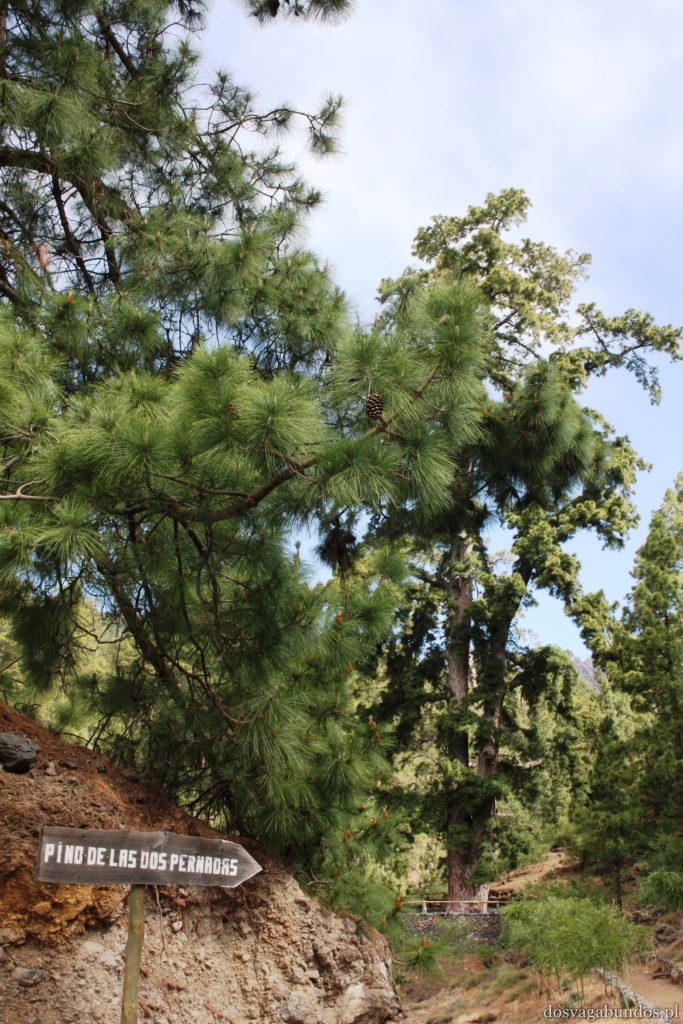
Ponieważ wypożyczyliśmy samochód na prawie tydzień, mieliśmy okazję dość dokładnie zwiedzić wyspę. I z czystym sumieniem mogę stwierdzić, że zobaczyliśmy prawie wszystko. Począwszy od niesamowitych, iście marsjańsko-kosmicznych widoków w Parku Narodowym Teide, otaczającym słynny wulkan, przez kolonialne miasteczka, pełne urokliwej zabudowy, ogromne przestrzenie niekończących się pasów wodnych, zarówno piaszczyste jak i kamieniste plaże, pomniki sakralne i rzeźby przedstawiające starożytnych przywódców, egzotyczne plantacje, rozpadające się domki, piękne pałace, gigantyczne hotele i klocki a’la bloki z lat ’70. Totalny miszmasz, który powoduje, że nigdy nie wiadomo na co się w danym momencie natrafi. Człowiek jest zresztą często zaskakiwany napotykanymi obiektami także z tego względu, że większość czasu zastanawia się czy przeżyje kolejną serpentynę nad urwiskiem, więc nie w głowie mu analiza rodzaju mijanego krajobrazu, lecz prędzej zaklinanie rzeczywistości. Drogi są dobre, ale straszliwie kręte, no i położone na przedziwnych wysokościach. Nie należy się tym jednak zrażać – kwestie bezpieczeństwa wpływają jedynie na czas dojazdu do celu, a nie zasadność samych podróży. Mniej wprawni kierowcy powinni po prostu uświadomić sobie, że trasy bywają trudne i w związku z powyższym poruszać się będą raczej w stylu Jasia Fasoli, jadącego na zakupy Mini Morrisem, a nie Krzysztofa Hołowczyca na torze wyścigowym. Wypożyczenie auta rekomendujemy z czystym sumieniem – w przeciwnym wypadku Teneryfę kojarzyć będziecie parkami rozrywki typu Siam czy Loro (ten drugi hejtujemy, bo jego fantastyczność opiera się na męczeniu zwierząt w jakiś durnych pokazach akrobatycznych).
4. Idealne warunki do uprawiania sportów wodnych
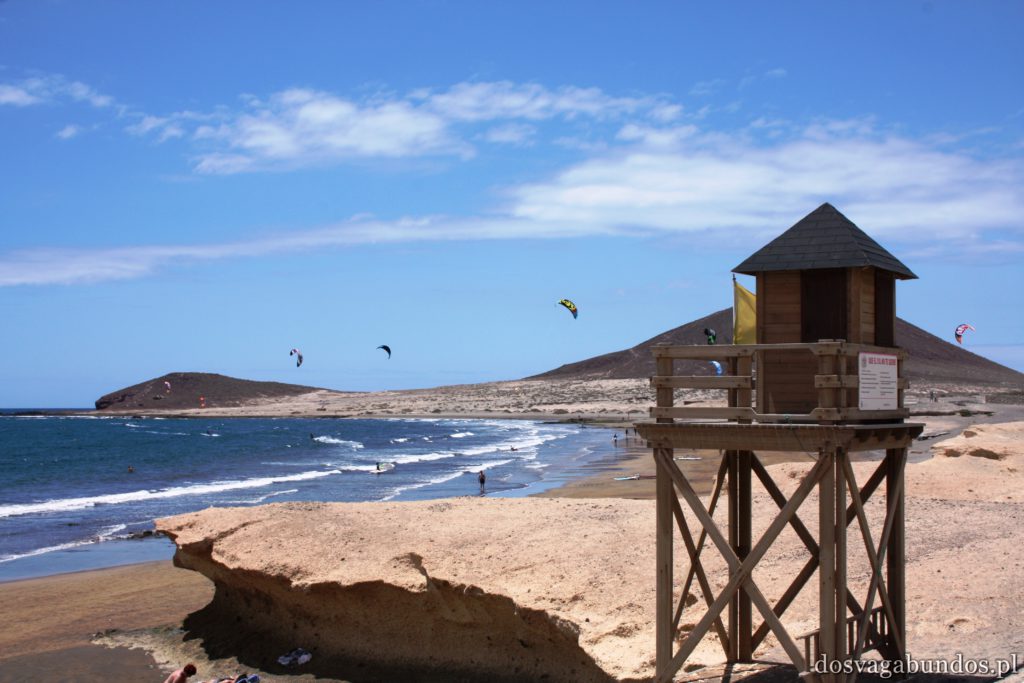
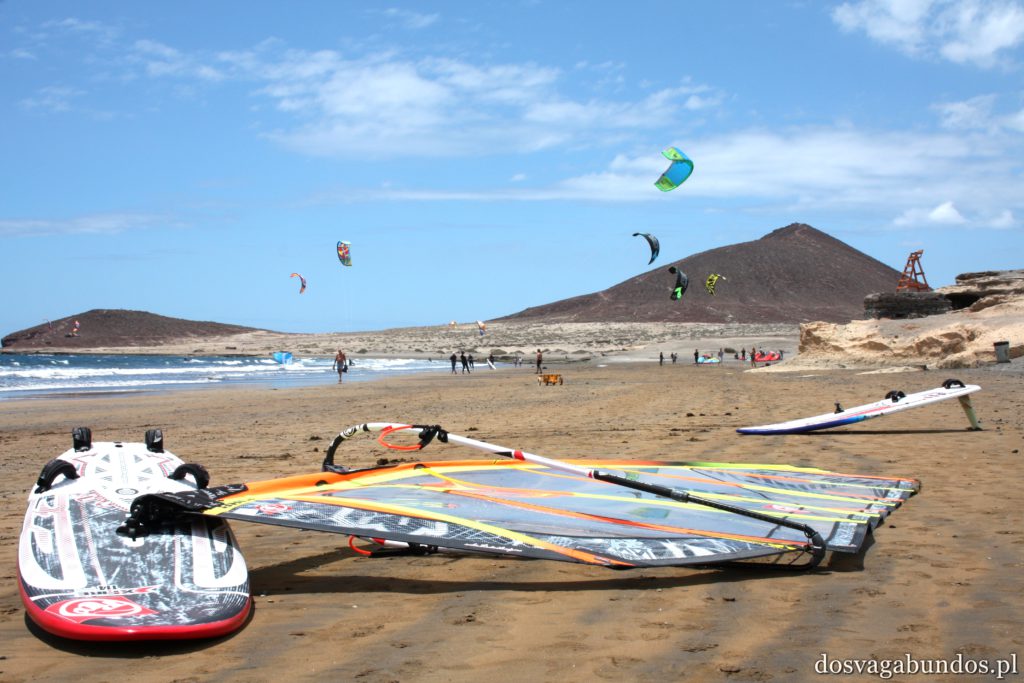
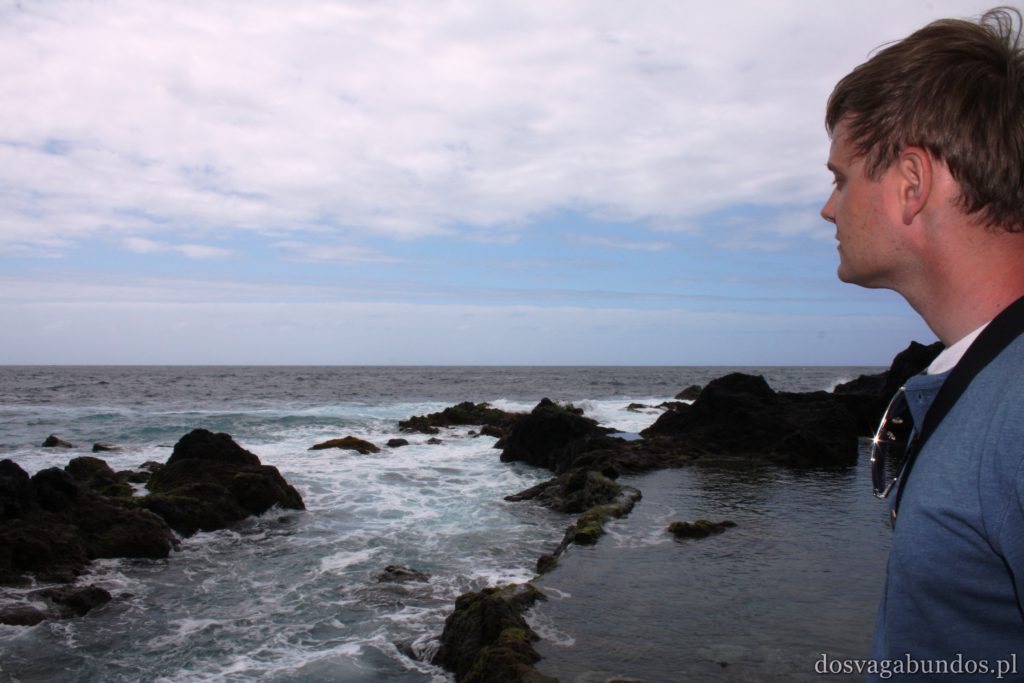
Położona nieopodal naszego hotelu mieścina El Medano, a dokładnie mieszcząca się w niej plaża, to prawdziwa mekka wind i kitesurferów. Co do zasady można tam spędzać czas również w inny sposób, tak sportowy, jak i badawczy czy spacerowy, jednak zdecydowaną większość osób na kilometr kwadratowy stanowią tam amatorzy wszelkiego rodzaju desek pływających. Dzięki temu jest bardzo kolorowo, energetycznie i młodzieżowo. Żałujemy niesamowicie, że w tamtym czasie nie mieliśmy za sobą kilku lekcji pływania na latawcu – za mało było czasu na naukę od podstaw. Patrzyliśmy więc z zazdrością na wszystkich zajawkowiczów w piankach i boardshortach, którzy wyczyniali istne akrobacje, tak w powietrzu, jak i na wodzie. Napotkaliśmy też dużo osób ćwiczących na lądzie – nie wiemy czy przygotowywali swoją formę na kite’a czy po prostu chcieli zadbać o ciało. Generalnie sport wyzierał tam z każdej strony, co w ostatecznym rozrachunku spowodowało, że zrezygnowaliśmy z planowanych lodów i wróciliśmy do samochodu, popijając niegazowaną wodę (no bo jak to tak może być, że wszyscy trenują, a my się obżeramy). Ponieważ grafik całego wyjazdu mieliśmy bardzo napięty, nie zostawiliśmy sobie za dużo czasu na kąpiele, a zdecydowana większość naszych kontaktów z wodą ograniczała się do wpatrywania w jej wzburzoną taflę (znowu zabrzmiało jak Pałlo Coejlo, bleh). Obiecaliśmy sobie jednak powrót na tamtejsze plaże (nie tylko El Medano zapewnia rewelacyjne warunki) i 100% oddanie się sportom wodnym, które obydwoje uwielbiamy.
5. Wspaniała fauna i flora
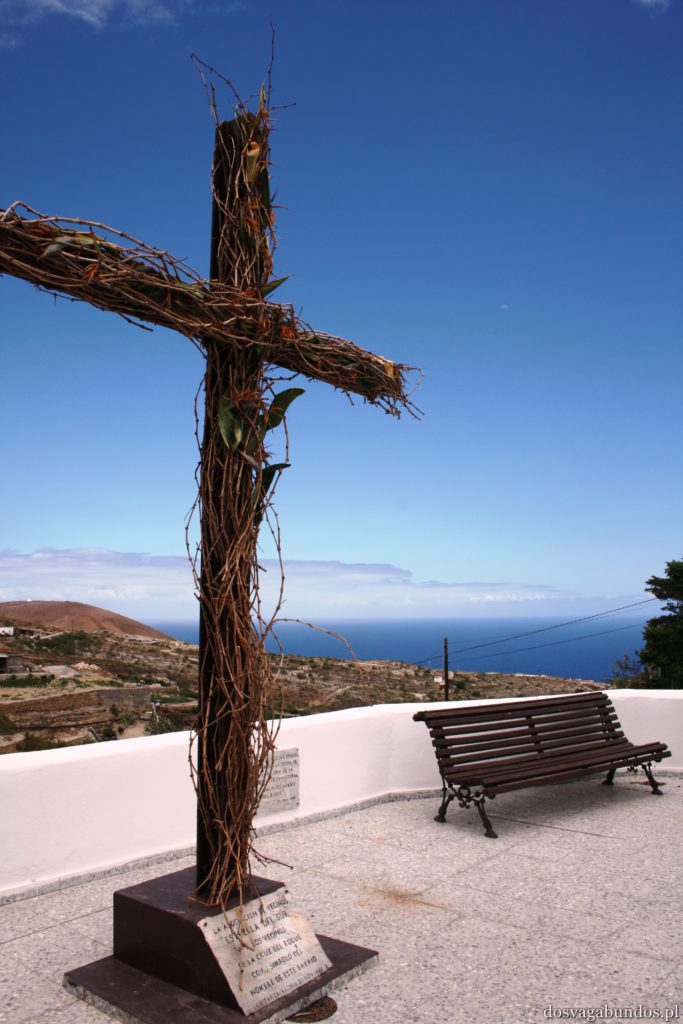
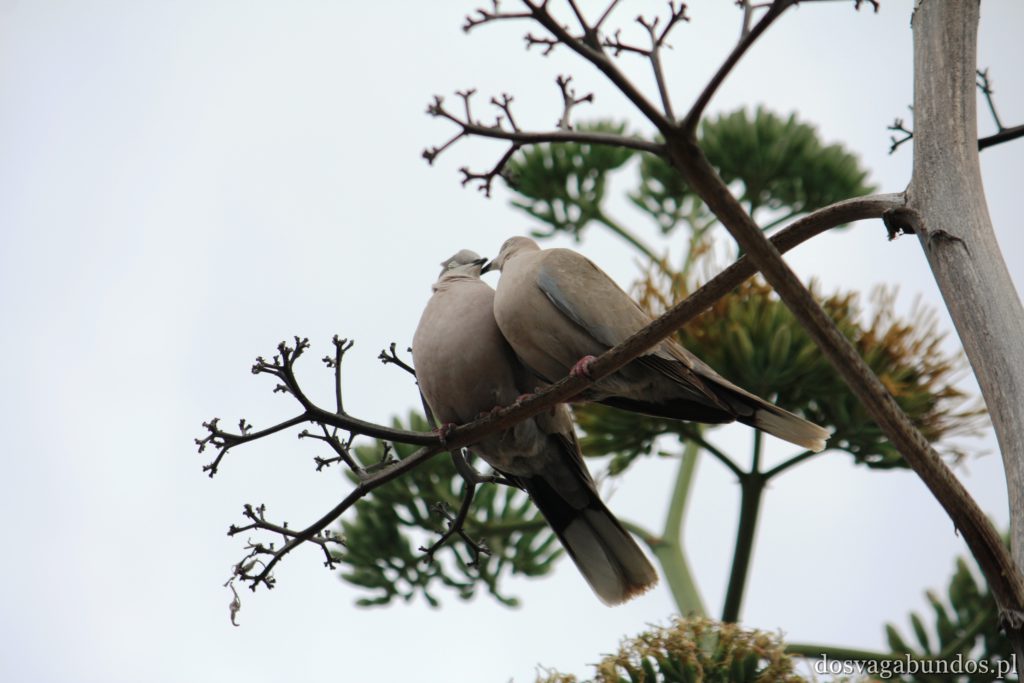
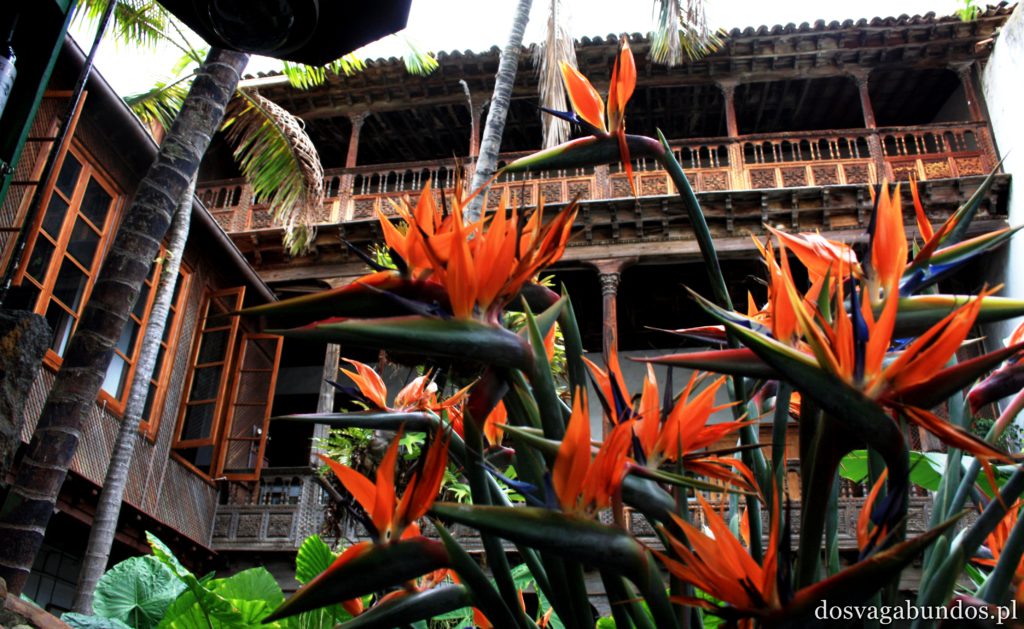
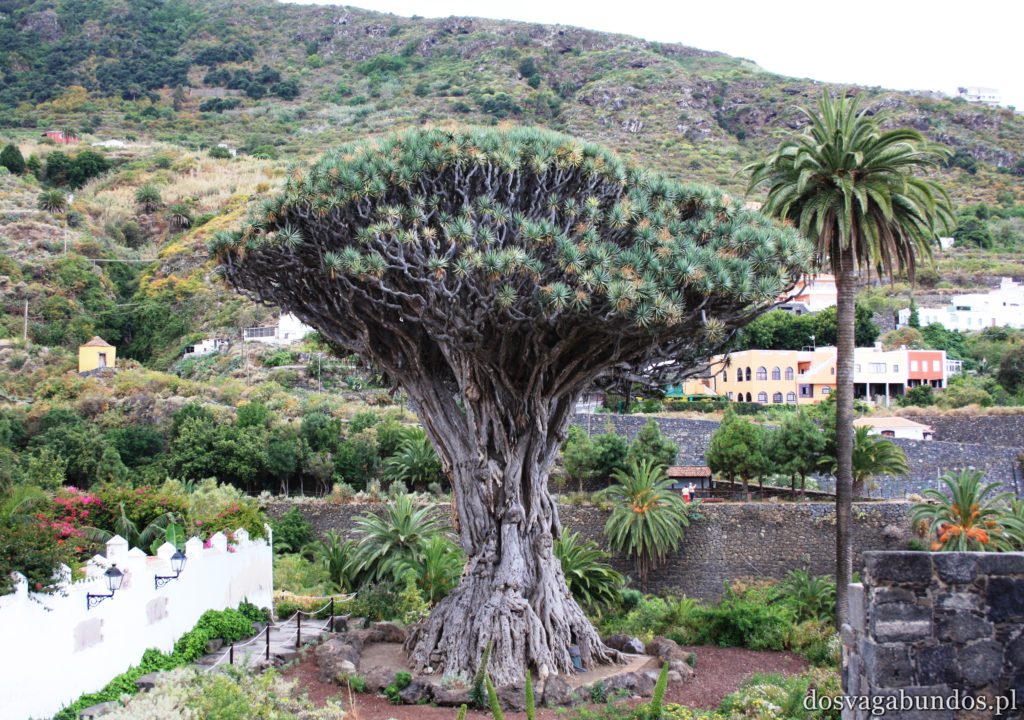
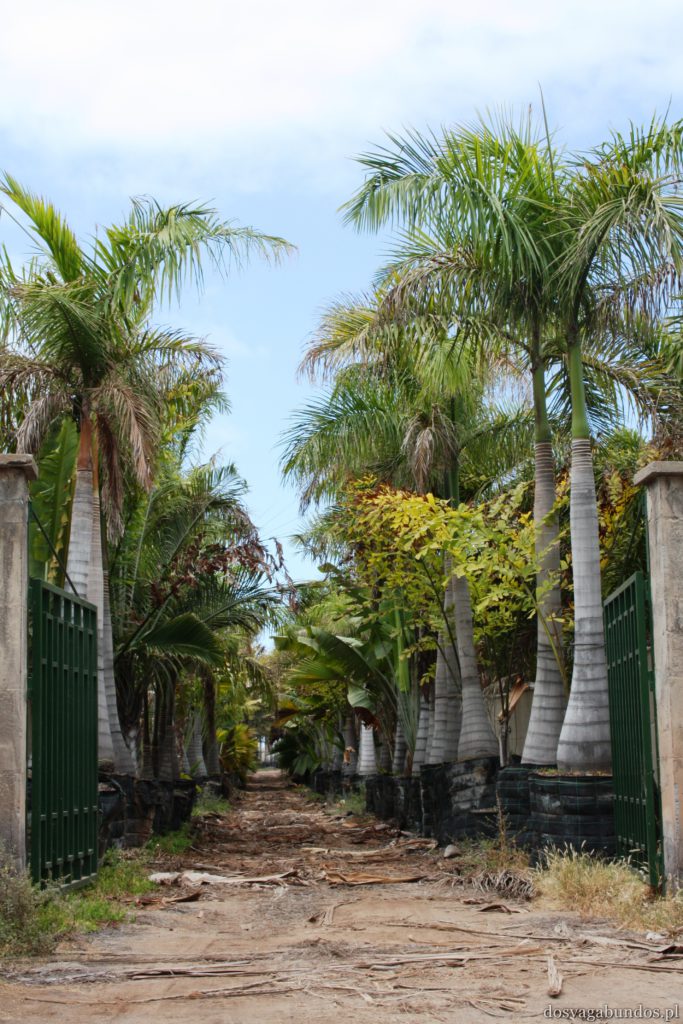
Podobno jeśli chodzi o Wyspy Kanaryjskie to najpiękniejszą roślinnością może się poszczycić Gomera. Nie wiemy, nie byliśmy, ale musi być w takim razie naprawdę zjawiskowa, bo to, co zobaczyliśmy na samej Teneryfie i tak nas wystarczająco zachwyciło. Zresztą jeśli chcecie, bez problemu dostaniecie się na pozostałe przedstawicielki “kanarów” – łódek jest dużo,pływają często a i odległości są na tyle bliskie, że warto się wybrać na taką krajoznawczą wyprawę. My akurat wybraliśmy rejs w poszukiwaniu delfinów z firmą o wdzięcznej nazwie “Jezus”. Udało nam się zobaczyć co prawda tylko kawałek płetwy jednego z nich (zupełnie inaczej niż w Egipcie, gdzie napotkaliśmy na całe stado tych pięknych ssaków), ale i tak było fajnie. Wracając do flory- można się w niej zatopić. Wszędzie pełno kolorowych kwiatów różnego rodzaju (nie wiem jak się nazywają, znam w zasadzie tylko róże, tulipany i stokrotki), ogromne drzewa, w tym sięgające nieba sosny, stare draceny, których wiek dochodził czasami i tysiąca lat, porobione z wielobarwnych płatków kompozycje, niekoniecznie w wazonach, ale i na chodnikach, w oknach, ulicznych schodach. Pięknie przystrzyżone klomby i alejki w turystycznych miejscowościach i endemiczna roślinność wokół wulkanu. Do tego motyle, ptaki każdej maści, mnóstwo psów na smyczach (większość przyjechała ze swoimi właścicielami w celach turystycznych!), konie, osiołki…Można by rzec – safari po europejsku.




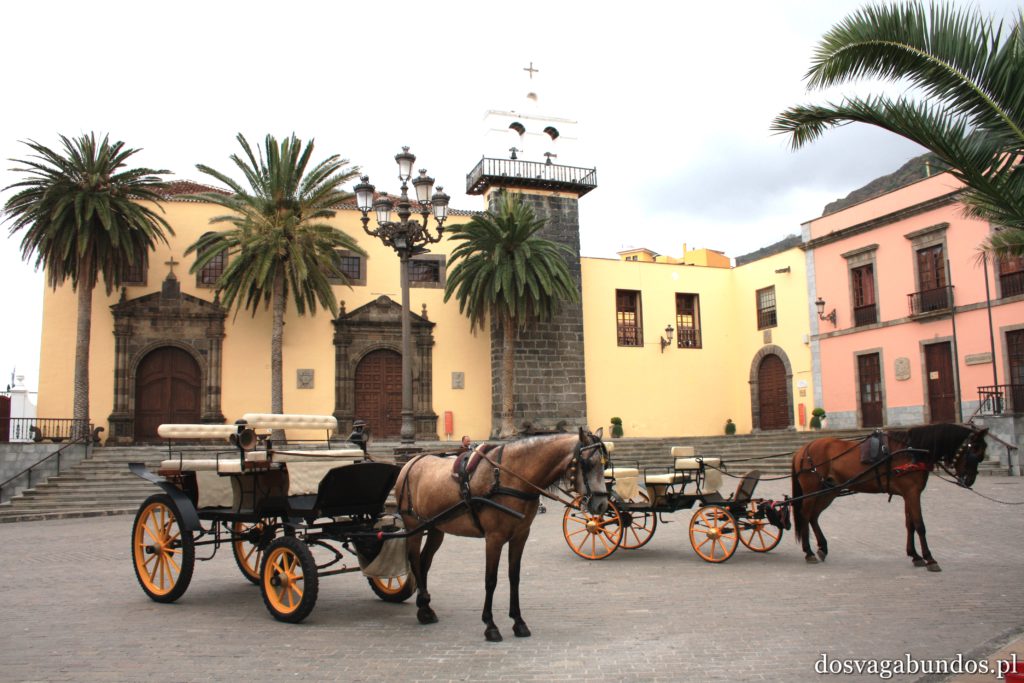























































Copper scrap customs clearance Copper scrap volume forecasting Efficient copper scrap utilization
Scrap aluminum reclamation Aluminium sustainability initiatives Aluminium scrap procurement
Copper scrap exporters Copper wire scrap suppliers Copper scrap sorting techniques
Copper scrap reprocessing Copper scrap valuation Copper recovery solutions
Copper scrap value Value of Copper scrapCopper scrap importers Innovations in Copper scrap recycling
Copper scrap export documentation Copper scrap cleaning Copper scrap recycling value
Scrap metal reclamation handling Ferrous material stakeholder communication Iron reclamation solutions
Foundry ferrous metal recycling, Iron scrap reclamation, Scrap metal trade negotiations
Scrap metal sorting Aluminium recycling resource optimization Aluminium waste emissions
Metal disassembling, Environmental benefits of recycling aluminum cable, Scrap metal recovery management
Scrap metal lifecycle management Scrap aluminium market assessment Scrap aluminium repurposing
Scrap metal import regulations, Benefits of recycling aluminum cable scrap, Circular economy metal practices
Metal recyclable waste solutions Aluminium scrap repurposing strategies Aluminum scrap pricing
Scrap metal reutilization and recycling, Aluminum cable shredding, Metal utilization
Scrap metal reprocessing Aluminum scrap recycling best practices Aluminum scrap legislation and regulations
Scrap metal sustainability practices, Aluminum cable scrap repurposing ideas, Metal waste recycling
Metal recovery and reclamation solutions Aluminium scrap material traceability Scrap aluminum yard
Metal recovery solutions center, Aluminum cable scrap weight, Scrap metal recycling and reclamation
Scrap metal material testing Aluminum scrap legislation and regulations Aluminium scrap extraction
Scrap metal processing center, Aluminum cable refurbishment, Scrap metal reprocessing and recovery
Copper carbonate recycling Copper scrap alloying Copper scrap energy efficiency
Scrap metal separation, Copper scrap material handling, Scrap metal volume assessment
Copper scrap material handling Copper is widely used in electrical applications, including wiring, because of its excellent electrical conductivity. In fact, copper is one of the most conductive materials known, surpassed only by silver and gold. The reason copper is such a good conductor is its unique atomic structure. Like all metals, copper has a lattice structure, which is composed of tightly packed atoms. However, in copper, the outermost electron in each atom is not tightly bound to its nucleus, but is instead free to move through the crystal lattice. These free electrons, commonly referred to as “electron sea”, are able to move easily through the lattice, which makes copper an excellent conductor of electricity. In addition to its high conductivity, copper is also very ductile and malleable, making it easy to shape into wires and other components. It is also highly resistant to corrosion, which is important in electrical applications where wires are exposed to the elements. Another advantage of copper wires is their low resistance, which means that less electrical energy is lost as heat as it flows through the wire. This is important, particularly in high-power applications, where efficiency and loss reduction are critical. Finally, copper is also relatively inexpensive and widely available. These factors combine to make copper the material of choice for electrical wiring worldwide Metal waste collection solutions Copper scrap resale value Scrap copper prices Waste water treatment in copper recycling Copper alloy refining Recycling yard management
Copper anode scrap acquisition In a recent study, researchers analyzed ice cores from Greenland and found evidence of ancient copper smelting pollution dating back to Roman and medieval times. The study sheds light on the impact of human activity on the environment in the past and provides insights into the history of early metallurgy. Copper smelting is a process used to extract copper from its ore, typically involving heating the ore with a reducing agent such as charcoal or coal. The process releases a range of pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, arsenic, and heavy metals such as lead and copper. The researchers analyzed ice cores from Greenland, which act as a sort of historical archive of atmospheric pollution. The ice cores contain layers that reflect changes in atmospheric composition over time, including the deposition of pollutants from human activity. By analyzing these layers, the researchers were able to identify spikes in copper concentrations that corresponded with periods of increased copper smelting activity in ancient Rome and medieval Europe. The researchers also identified increased levels of lead, sulfur, and arsenic during these periods, indicating that these pollutants were also released during copper smelting. The study underscores the long history of human impact on the environment and the importance of understanding this history in order to address modern environmental challenges. It also provides important insights into the history of metallurgy and its role in shaping human societies. Overall, the study highlights the value of interdisciplinary research that combines historical, archaeological, and environmental data to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the past. By doing so, we can better understand the impact of human activity on the environment and develop more effective strategies for mitigating this impact in the future Metal recovery and reclamation solutions Local copper scrap buyers Copper scrap reception Environmental copper disposal Copper scrap quality assurance Metal scrap recovery and reprocessing
Metal waste packaging Scrap metal storage Iron scrap collection services
Ferrous material integrity, Iron scrap reprocessing plants, Metal scraps
Metal reclamation and reutilization solutions Ferrous material buying Iron scrap shearing
Ferrous scrap risk management, Iron waste recovery plant, Scrap metal trade regulations
Scrap collection network Ferrous material recycling social responsibility Iron reclamation and recovery center
Ferrous material shredders, Iron scrap recycling best practices, Metal reprocessing and reclaiming
Metal recovery and reprocessing Ferrous material scrap appraisal Iron scrap salvage
Ferrous metal recycling process, Iron scrap packaging, Metal waste collection
Scrap metal export Ferrous material recycling sustainability Scrap iron transportation
Ferrous material tracking, Iron salvage and reclamation, Metal scrap collection services
http://susan.webadsky.net/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=6458
As a Newbie, I am permanently searching online for articles that can benefit me. Thank you
You completed a few fine points there. I did a search on the topic and found most folks will have the same opinion with your blog.
I genuinely appreciate your piece of work, Great post.
Thank you for some other informative website. Where else could I am getting that type of info written in such a perfect manner? I have a project that I’m just now running on, and I have been on the look out for such information.
Hi there, I discovered your site by the use of Google at the same time as looking for a related topic, your website got here up, it appears to be like good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.